This article is not yet complete. If you have any questions, please feel free to ask in the Discussion.
Also, if you would like to contribute to this article, feel free to open a Pull Request on our GitHub Repository.
Deploy NestJS App
Deploy your NestJS app in Zeabur.
Step 1: Create NestJS app (optional)
You can use NestJS CLI to create a new app.
Open your terminal and run the following command:
npm install -g @nestjs/cliThen, create a new app:
nest new <your project name>You can also clone a starter project from our GitHub repository.
git clone https://github.com/zeabur/nestjs-template.git <your project name>Then, install the dependencies:
pnpm installStep 2: Setup environment variables
You can skip this step if you are using the starter project from our GitHub repository.
In Node.js applications, it’s common to use .env files, holding key-value pairs where each key represents a particular value, to represent each environment.
NestJS provides a package called @nestjs/config to help you manage your environment variables.
pnpm add @nestjs/configOnce the installation process is complete, You can import the ConfigModule into src/app.module.ts and control its behavior using the .forRoot() static method.
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common'
import { ConfigModule } from '@nestjs/config'
@Module({
imports: [ConfigModule.forRoot()],
})
export class AppModule {}Now, you can set up your port in src/main.ts
import { NestFactory } from '@nestjs/core';
import { AppModule } from './app.module';
async function bootstrap() {
const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule);
await app.listen(process.env.PORT || 3000);
}
bootstrap().then(() =>
console.log(`Application is running on: ${process.env.PORT || 3000}`),
);Step 3: Deploy
Click on Add new service button, then choose Deploy your source code.
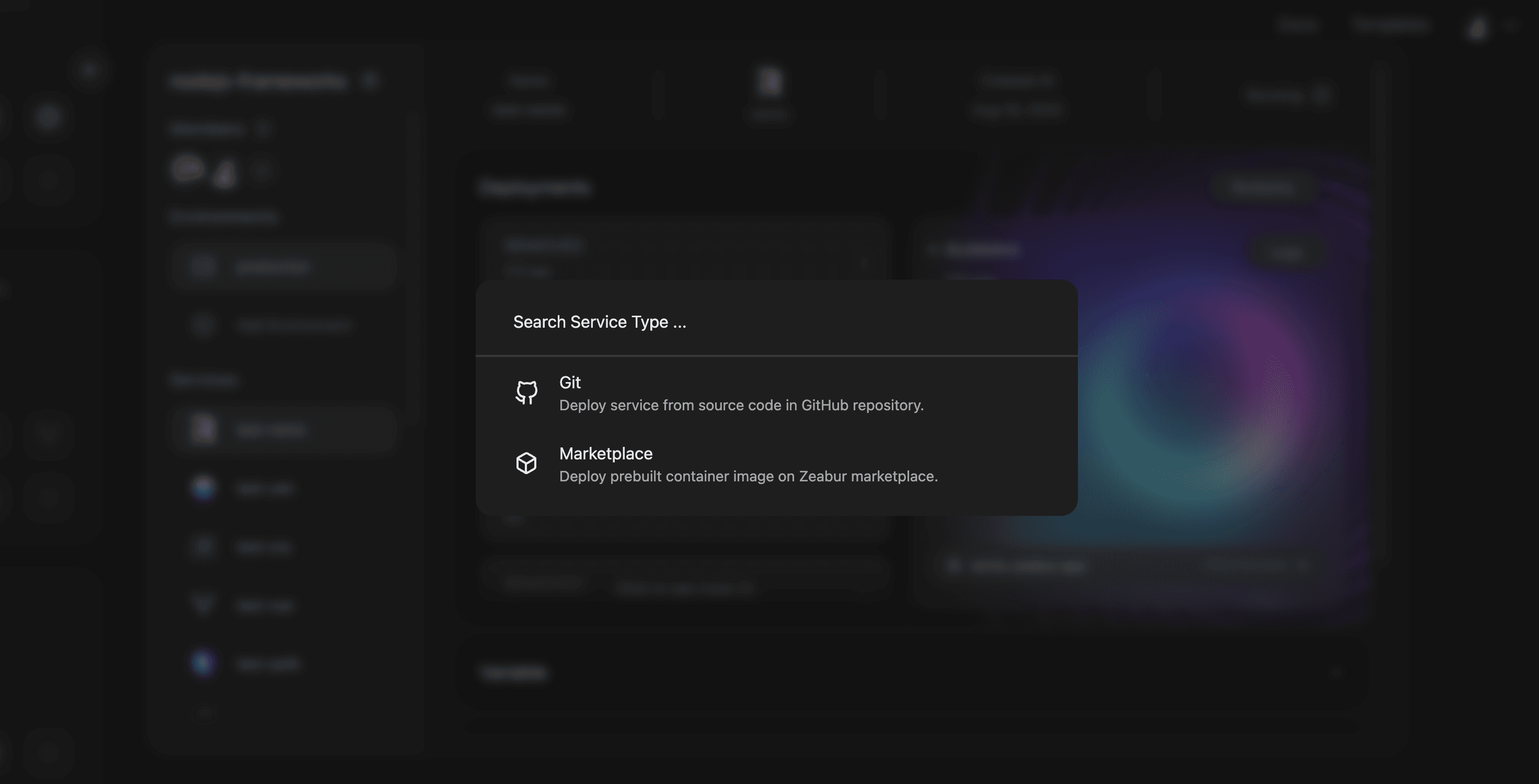
Search for your NestJS App repository, click on import, your NestJS App will start deploying.