Deploying with Dockerfile
Normally, you don’t need to write a Dockerfile by yourself. Zeabur currently provides fast deployment methods for various popular frameworks, but if your project is not using these frameworks or you want to define your own deployment method, you can use a Dockerfile to deploy it.
Creating a Dockerfile
Create a file named Dockerfile or dockerfile in the root directory of your project and write your deployment method in it. Finally, make sure you have exposed the corresponding PORT.
Zeabur will automatically detect if your project has a Dockerfile. If so, it will deploy your project using Docker.
After the deployment starts, you can see the Docker icon above, which means your project has been deployed using Docker.
Deploying without using Dockerfile
If your project has a Dockerfile but you do not want to use this Dockerfile on Zeabur (for example, letting Zeabur decide the best deployment method of this project), you can set ZBPACK_IGNORE_DOCKERFILE=true in the environment variables, or add the following to zbpack.json:
{
"ignore_dockerfile": true
}Zeabur will then ignore your Dockerfile and automatically determine the deployment method.
Environment Variables
If your Dockerfile needs to use environment variables, you can click Environment Variables on the service page to add them. For more settings, please refer to Environment Variables.
If your Dockerfile is written in one stage, or if your environment variables only need to be used in the final stage, you don’t need to manually write ENV. Zeabur will automatically add it for you.
ARG
However, if your Dockerfile is written in multiple stages (multi-stage), and you need to set environment variables before building, you can use ARG to set them.
Here, we take nodejs and nginx as an example to write a Dockerfile for deployment.
FROM node:18-alpine AS builder
WORKDIR /app
COPY . .
## The `BUILDTIME_ENV_EXAMPLE` here will be set before building automatically
ARG BUILDTIME_ENV_EXAMPLE
ENV BUILDTIME_ENV_EXAMPLE=${BUILDTIME_ENV_EXAMPLE}
RUN npm install && \
npm run build
FROM nginx:alpine
COPY nginx.conf /etc/nginx/conf.d/configfile.template
COPY --from=builder /app/dist /usr/share/nginx/html
ENV \
PORT=8080 \
HOST=0.0.0.0
EXPOSE 8080
CMD sh -c "envsubst '\$PORT' < /etc/nginx/conf.d/configfile.template > /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf && nginx -g 'daemon off;'"Specifying Dockerfile to Deploy
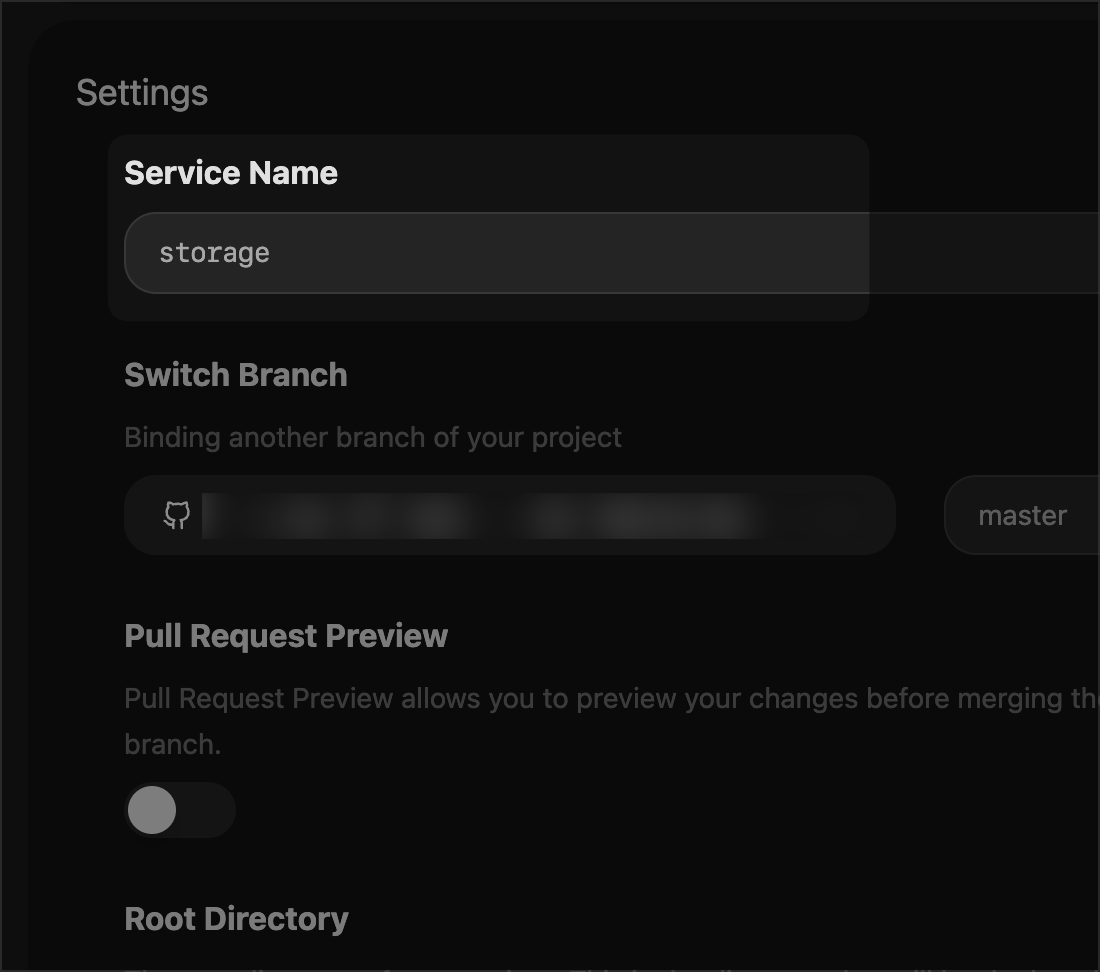
To deploy a project using a specified Dockerfile, name the Dockerfile as [service-name].Dockerfile or Dockerfile.[service-name]. For instance, if you have a Dockerfile.storage file in your project and your service name is storage, Zeabur will deploy the storage service using this Dockerfile.
You can also specify the ZBPACK_DOCKERFILE_NAME environment variable or add the following to zbpack.json:
{
"dockerfile": {
"name": "storage"
}
}For example, if you set ZBPACK_DOCKERFILE_NAME=storage in your service, Zeabur will use Dockerfile.storage as the Dockerfile to deploy the storage service.
Docker Compose
Zeabur currently does not support deploying from Docker Compose YAML.
You can convert your Docker Compose file into a Zeabur Template YAML. For details, see Creating Templates from YAML. If you need assistance, feel free to contact us at community.